Weather intelligence for the future: Crafting a strategic enterprise approach to changing environmental conditions
Continue readingSevere storms affect business operations and consumers everywhere, costing an average of USD 10 billion in damages and taking about 500 lives each year. Constituents rely on weather data to assess how to prepare for storms.
Meteorologists are tasked with providing weather predictions to their viewers to help them make the most informed decisions. Accurate weather data is an important component in getting viewers the information they need to better prepare communities with recommendations on how to remain as safe as possible during severe weather events.
What is severe weather?
When discussing the weather, forecasters often cite the state of the atmosphere, including elements such as temperature, clouds and wind. Severe weather refers to the dangerous effects created by these changes in the atmosphere that result in tornadoes, extreme thunderstorms or blizzards.
Severe storms—often packed with heavy rains, strong winds, hail and lightning—can wreak havoc in a short time. When these fast-moving, highly localized storms move through a region, people and businesses need to be aware and take swift action.
Across industries, The Weather Company has the tools necessary to provide timely, accurate data that helps businesses keep employees safe, better protect assets and convey vital information effectively. Our tools help you and your business prepare for the storm and react faster, all while minimizing disruptions and impacts using severe weather forecasting.
How does climate change make weather more extreme?
As the atmosphere warms, the effects of violent storms are becoming more extreme. An analysis by Carbon Brief revealed that 70 percent of the 405 extreme weather events and trends included in their map of attribution studies were found to be made more likely or more severe by human-caused climate change.
In August 2020, Hurricane Isaias wreaked havoc as it traveled along the East Coast, causing damage that had not been seen since Hurricane Sandy. In California, the wildfire season is beginning earlier and ending later. California exceeded 4 million acres burned by wildfires in 2020. More than 8,200 fires have consumed more than double the previous record, fire officials said.

The tools needed to forecast severe weather
There are various tools in a meteorologist’s toolkit to predict when violent storms are coming, including partnerships across the world and improvements in forecasting models.
These tools involve gathering weather data, making future predictions, and communicating those predictions.
Gathering weather data
When gathering weather data, it’s important to leverage various sources of information to make the best prediction possible.
Observing stations
In order to gather the vast amounts of data needed to make accurate weather predictions, observing stations are located around the globe. Many of the best gathering stations are located at airports, which require accurate weather information to keep passengers and crew safe during takeoff and landing. However, this data may not be localized enough for specific industries that require more granular details.
Weather information is shared from these stations across the globe through channels such as the United Nations. The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 193 Member States and Territories, which verifies that the data gathered from these stations is consistent across nations.
Weather satellites
Weather satellites orbit the earth and collect various points of data related to the temperature of the earth below. There are two kinds of weather satellites that are used by the National Weather Service to collect data:
- Polar Orbit: These kinds of satellites move from north to south along a specified path. They are able to record data twice from the entire planet in a single day. The National Weather Service currently has two of these satellites in orbit.
- Geostationary: These kinds of satellites are fixed to a specific location. In the United States, the National Weather Service has two, with one focusing on the East Coast and one the West Coast. They travel at the same speed as earth, so they only collect data from this one location. In the cases of severe weather, these satellites can take images of a small area every minute.
Weather radar
Forecasting severe weather also involves utilizing weather radar to determine the motion and intensity of precipitation. Energy pulses or radar beams are sent into the atmosphere to determine the type (for example, snow or hail). Weather radar can also be used to determine wind speed and predict the formation of tornadoes. It’s a valuable tool for meteorologists.
Weather balloons
Weather balloons are used to gather information, such as temperature, from higher altitudes. Radiosondes are the devices attached to these balloons that gather the appropriate data. These balloons can reach as high as 24 miles before disintegrating.
IoT data and sensors
With the emergence of IoT, there are ample opportunities to incorporate new data sources for accurate weather predictions. By leveraging IoT data and sensors from smartphones and self-driving cars, weather-forecast data can be more localized, which allows for more actionable insights and predictions for members of the community.
How to forecast severe weather
Weather predictions contain various components and steps. Forecasts need to be changed by slight changes in things like temperature, and wind direction. It is important for meteorologists to constantly assess the data to determine how these changes will affect their predictions and communities.
Different tools are needed to track these changes and scientists leverage weather radar, satellites, forecasting models, among others to predict weather patterns.
Analog method
This method involves looking at historical weather and trends to find patterns and make predictions. However, this strategy can be difficult to accurately apply, because no two storms are the same. Additionally, with the emergence of climate change, weather patterns may change.
Synoptic method
The synoptic method is when meteorologists systematically study recent weather forecasts from a vast area in order to forecast the weather. Current weather conditions are linked to similar scenarios from the past, and then predictions are made based on the premise that the current scenario may behave similarly to the situation in the past.
Statistical Method
Regression equations and other advanced relationships are used in the statistical method to make predictions between various weather elements and the subsequent climate. Weather predictions are usually made based on potential physical interactions with the predictants.
Trend forecasts
This forecasting method assumes that unless there is evidence to the contrary, weather patterns will continue to travel at the same speed and in the same direction.
Forecasting models
Forecasting models incorporate data sets, including inputs from weather radar and historical trends, to predict the course of the storm. With machine learning techniques, these models become more accurate over time. They run millions of equations to determine the course of the storm over short and long timeframes.
With the added capabilities from The Weather Company, these models can extend beyond making storm predictions and translate these insights into actionable steps to help communities prepare (for example: helping utility companies determine which part of the grid may be most likely to face a power outage.) Additionally Forecast Watch analyzed 140 million forecasts between 2017-2021 and determined that The Weather Company had the most accurate weather forecasting technology.
Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
These particular models utilize mathematics and computers to make predictions on the weather based on the current state of the atmosphere. Though first conceptualized in the 1920s, this way of forecasting did not gain traction until the 1950s, when computers could be applied to mathematical formulas. In order to calculate the forecast for one day, millions of equations need to be solved. Before the advent of the computer, this was an impossible task for meteorologists to undertake.
What are the 3 kinds of forecasts?
There are few ways to forecast weather. Below are some of the most common ways to determine the weather forecast.
- Short-range forecasts: predictions made between 1-7 days before they happen. This is the most accurate type of forecast.
- Medium-range forecasts: predictions given between one week to four weeks in advance.
- Long-range forecasts: predictions given between one month and a year in advance.
What are the 5 risk levels for violent weather?
Severe weather consists of 5 different risk categories: marginal, slight, enhanced, moderate and high.
- Marginal: This consists of isolated, short-lived thunderstorms that have a limited intensity. Usually they will have winds between 40-60 mph, as well as hail up to 1″, but be a low risk for tornadoes.
- Slight: This level involves scattered storms which are more severe, but also short-lived with isolated intensity. There may be 1-2 possible tornadoes, as well as strong winds and wind damage.
- Enhanced: A level 3, enhanced risk deals with numerous, persistent storms that include a few intense ones. These may produce a few tornadoes as well as wind damage.
- Moderate Risk: A level 4 will have widespread, long-lived and intense severe storms. These may include strong tornadoes, large hail, and widespread wind damage.
- High Risk: These storms are widespread, long-lived and extremely intense. They usually also involve a tornado outbreak or significant wind damage.
Types of severe weather: An overview of violent storms

Severe thunderstorms
According to the National Weather Service, a thunderstorm is considered severe when it creates hail that is 1 inch in diameter or has wind speeds 58 mph or greater. About 10 percent of annual thunderstorms in the United States are categorized as severe. There are many dangerous aspects to these weather events, whether it be flash flooding, hail or lightning.
How do meteorologists predict thunderstorms?
Meteorologists use a wide variety of tools to predict if a thunderstorm will occur. With satellites, they can track the movement of clouds and temperature. Through weather radar, they can determine the likelihood of a tornado or hail. These tools can also track these storms after their initiation and help meteorologists follow their movement.
Meteorologists also have forecasting models at their disposal, which take these various inputs and help determine the likelihood of a weather event occurring. Sophisticated models can take data from a wide variety of inputs to determine the most likely scenario.
A severe weather alert is also issued throughout the United States three times a day, which details the likelihood of a thunderstorm occurring in specific parts of the country. For cases of extreme weather, The National Weather Service will issue an alert to affected communities.
What causes these kinds of severe storms to happen?
Thunderstorms are usually created via a combination of moisture, atmospheric instability, and lift. Warm air, which is closer to the ground, will rise above colder, drier air. The rapid rising of air is needed for thunderstorm clouds to form. Water vapor further fuels the storm by propelling air even higher into the atmosphere.
What is the most dangerous kind of thunderstorm?
Supercell thunderstorms are generally considered the most dangerous type. They are characterized by mesocyclones, which is a large region of rotation. Supercell thunderstorms can lead to tornadoes, produce large hail, and cause lightning.
What is lightning and what causes it?
Lightning is a huge spark of electricity that can be created within and between clouds, the air and the ground. When water and ice are moving within a cloud, pressure starts to build. This is due to the warmer air currents moving the elements upwards, and gravity forcing them back down. This charges the particles in the cloud. When the negative and positive particles in the cloud seek to neutralize, and the air acting as an insulator breaks down, there is a discharge of electricity, also known as lightning. On average, NOAA reports that lightning strikes the US about 25 million times each year and injures hundreds in the process.
What are the types of lightning?
There are three main kinds of lightning. These include:
- Intracloud
- Cloud-to-cloud (CC) or intercloud
- Cloud-to-ground (CG)
Intracloud lightning occurs within the thundercloud since the cloud has both negative and positive charges. This is the most common form of lightning. This discharge can also happen between clouds, which is known as cloud-to-cloud (CC) or intercloud lightning.
Cloud-to-ground (CG) lightning is the least common type of lightning and occurs when electricity strikes the ground. Although CG lightning can be either charge, it tends to be negative.
Wildfires: how are they related to severe weather?
Wildfires are heavily influenced by the climate. Due to droughts caused by climate changes, the risk of wildfires is expected to increase. Since 2000, an average of over 72,000 wildfires have destroyed 7 million acres of land each year in the US.
What are wildfires?
Wildfires are unplanned and out-of-control fires. They burn through forests, vegetation, and are susceptible in areas where vegetation is drier. They happen around the world, including the US, Canada, and Australia.
What causes wildfires?
Ten-fifteen percent of wildfires occur naturally. This includes lightning strikes and severe thunderstorms. Eighty – ninety percent are caused by humans. Through dry vegetation, drought, and other factors related to climate change, these wildfires can quickly grow out of control.
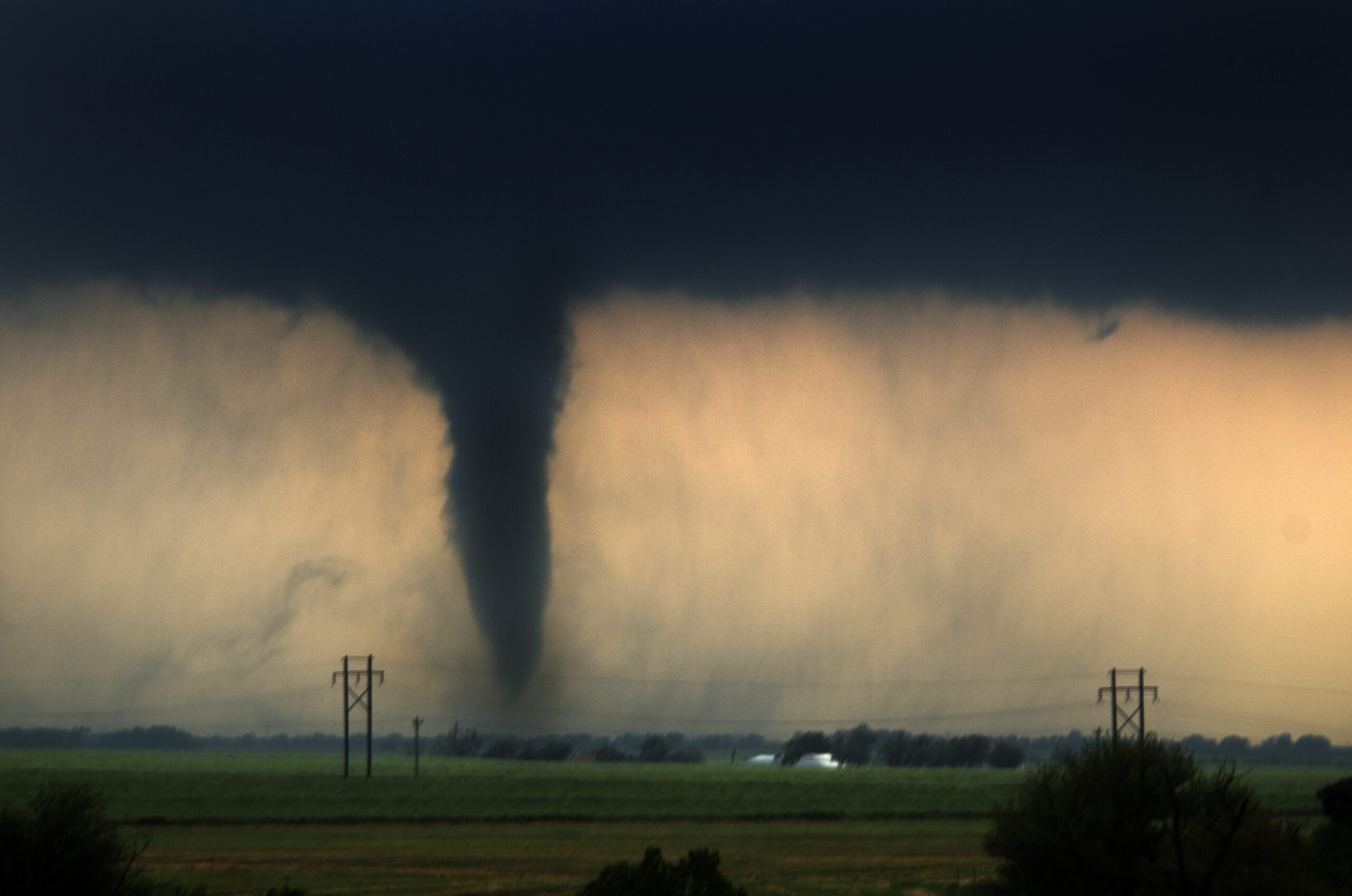
An overview of tornadoes
Tornadoes are columns of rotating air that usually result from a severe thunderstorm. Tornadoes have clouds, as well as strong wind, rain, and hail. They travel at speeds of about 10 to 20 miles per hour. Wind speeds can reach up to 200 miles per hour and the results of these weather events can be devastating for communities and business owners.
What creates dangerous weather systems like tornadoes?
Tornadoes are formed in large thunderstorms, where air becomes unstable due to the shifting of warm and cold air. Although scientists know the components of a tornado, it is still difficult to predict them. The process, in which a tornado forms, is still a mystery.
How are tornadoes forecasted?
In 1973, tornadoes were first identified on weather radar before their formation. This breakthrough has allowed meteorologists to better prepare communities prior to these extreme weather events.
Meteorologists and other industry professionals can use Doppler radar to detect tornadoes. What is typically seen on the radar is a mesocyclone, which is an area of rotation often within a thunderstorm. These can span between 2 – 6 miles and can indicate the threat of an upcoming tornado.
What are the types of tornadoes?
There are two main categories of tornadoes—supercell and non-supercell. The first type develops from supercell thunderstorms and often results in more damage. Scientists do not yet understand why these kinds of tornadoes form, as only 20 percent of all supercell thunderstorms result in these severe weather events.
An overview of blizzards
Blizzards are storms that result in vast amounts of snow with little visibility and 35 mph winds. In particular, driving conditions can be dangerous because whiteouts can hinder a driver’s ability to see, leading to accidents.
How are blizzards forecasted?
For blizzards to develop, wind needs to move quickly, temperatures must be low, and humidity must be high. If the temperature isn’t cold enough, snow will melt once it hits the ground. A wide variety of tools are used to forecast if a storm will become a blizzard and the rate of precipitation, including satellites and Doppler radar. Weather forecast models are used to track blizzards and predict how they will progress.
What causes blizzards?
In order for snow to form, it must be cold higher in the atmosphere and on the ground. If the ground isn’t cold, snow doesn’t stick and will melt before accumulating.
Since cold air can’t retain a high level of moisture, warm air will need to rise above the clouds to form the snow. Additionally, blizzards require wind reaching at least 35 mph. The combined wind and snow must reduce visibility to one-quarter mile or less.
Blizzards can occur also without new snow forming. If wind reaches the designated speed and there is already snow on the ground, visibility can be reduced, making driving nearly impossible. These kinds of storms are known as ground blizzards.

Dust storms
Dust storms are a more unusual form of severe weather. They are characterized as a strong windstorm that carries sand or dust particles. These storms can be particularly damaging to the agriculture industry, ruining crops for farmers.
Hurricanes
Hurricanes, which are also known as cyclones, are also a type of extreme weather. Hurricanes are essentially giant, spiraling tropical storms. They must include strong winds over 160 miles per hour. They also include very heavy rains which can drop more than 2.4 trillion gallons of rain a day.
How do meteorologists categorize the severity of a hurricane?
The category of a hurricane (1-5) is determined by wind speed. Hurricane categories do not take other factors, such as rainfall and potential damage, into account. A lower category storm can create significant damage, particularly when the affected area does not have the proper infrastructure in place.
Flooding
Flooding can happen when there’s heavy rainfall in short periods of time. When large amounts of rainfall occur, water overflows its natural or artificial banks onto land. Floods can also occur when ocean waves come to shore, when snow melts too quickly, or when dams break. Flooding can cause damage with just a few inches of water. Additionally, extreme foods can cover rooftops of homes and cause mass evacuations. Floods can occur in minutes, days, weeks, or longer.
What is a flash flood?
Flash floods combine the destructive power of normal floods with incredible speed. Flash floods occur when the ground is unable to absorb heavy rainfall. They can also occur when water fills dry creeks or streams and the water floods overtop the banks. This causes rapid rises of water in short periods of time.
Where and when do floods occur?
Flooding can occur in every single U.S. state and territory. It is a threat that is experienced anywhere in the world that gets rain. Deaths from flooding are increasing globally. Since 2015, over 100 people have died every year due to flooding.
What areas are flash floods prevalent?
Highly populated areas are at a much higher risk for flash floods. Areas filled with construction of buildings, highways, and parking lots also increase runoff because this reduces the amount of rain absorbed into the ground.
Hailstorms 101
Hailstorms are characterized by balls of ice falling from the sky. These are generally formed in a thunderstorm and can damage windows, cars and other structures.
How does hail form?
Hailstorms form in cumulonimbus clouds, which are large mushroom-shaped clouds that are characteristic of a severe thunderstorm. Strong upward currents (also known as updrafts) must accompany these clouds, bringing water droplets up through the atmosphere. These droplets become ice, resulting in hail.

Don’t let a severe storm catch you off guard. Leverage our solutions and tools when violent weather approaches.
Advanced warning. Actionable information. Proactive alerting.
Severe storms—no matter the form they take—can develop quickly, change rapidly, and pack a punch. Heavy rains, wind gusts, lightning, hail (or any combination of elements) can put a field crew in danger and disrupt regular business operations.
The most accurate and timely information on these highly localized weather events needs to be communicated quickly. Whether it’s alerting field workers of lightning in their area, rerouting a flight or informing the public of storm details across multiple channels, businesses need specialized weather forecasting technology.
Broadcast media storm solutions
When a storm is in a local station’s coverage area, the latest severe weather information needs to be communicated across channels. People have always counted on their local TV station to provide severe storm information, but now broadcasters have to reach their audience on mobile apps and alerts, web and social media through stunning weather graphics and accurate weather forecasting technology. The Max Ecosystem is designed with efficiency in mind and allows teams to produce high-quality news videos and presenters to disperse information across multiple channels in just a few clicks—a critical need when a severe storm is approaching.
Additionally, by leveraging augmented reality solutions from The Weather Company, your team can better showcase the effects of violent weather to help your viewers visualize the impacts.
Contact us to learn more about our forecasting solutions for the media industry.
Frequently asked questions
Severe weather is caused by changes in the atmosphere in relation to temperature, wind or air pressure. These changes can result in tornadoes, blizzards, floods and ice storms.
While extreme weather and severe weather may sound like the same thing, they’re a bit different. Extreme weather is essentially any type of weather that is out of the norm for a particular area. Meteorologists will typically look to past historical weather data of that region to see whether or not the forecast falls within the range of what is considered normal.
Due to climate change, extreme weather events are increasing around the globe. Since 1880, the earth is up 1.01 degrees Celsius. Sea levels have risen 4 inches since January 1993. Record high temperatures have been on the rise in the United States since 1950.
Climate change is having a big impact on rising temperatures. In July 2022, London reached record-breaking temperatures, resulting in runways melting and train tracks lighting ablaze. During this same month, 100 million people faced extreme heat in the United States with states such as Oklahoma facing 115 degrees.
There are several types of extreme weather. These include:
- Tornadoes
- Hurricanes
- Blizzards
- Hail storms
- Floods
- Ice storms
- Heat
All severe weather can be dangerous. However, certain weather patterns have resulted in more lost property and lives than others. The largest number of deaths from US weather-related events are due to summer heat according to a 30-year average (1988 – 2017) from NOAA. Additionally, over the last several years, hurricanes Harvey, Maria and Irma, alongside the California wildfires, have had the most deadly outcomes.
Meteorologists use a variety of tools to predict severe weather events, including weather balloons, observing stations, and weather radar. Forecasting models are then applied to the data to predict upcoming storms.
Extreme weather can cause problems for drivers, if the roads are affected. Rainfall can impact roads and make it more likely for cars to hydroplane. Blizzards and ice can make road conditions slick. For broadcasters, it’s important to understand how extreme weather events can impact driving.
Let’s talk
To learn more about our professional weather and traffic software solutions for the media industry, contact our media experts today.
Contact us